A) perceived differences that are not likely to exist among your various options.
B) quality when quality cannot be easily judged.
C) inefficiency in markets characterized by recognizable brand names.
D) the quality of general lodging accommodations in Dhaka.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive market
A) usually has too many firms, reducing the economic profit of each firm to zero.
B) usually has too few firms, reducing the product variety for consumers.
C) may have too many or too few firms, and the government can intervene to achieve the optimal number of firms.
D) may have too many or too few firms, but the government can do little to rectify the situation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Entry by new firms into a monopolistically competitive market
A) creates additional consumer surplus.
B) imposes a positive externality on existing firms.
C) leads to the same externalities that are observed when new firms enter a perfectly competitive market.
D) increases the demand for existing firms' products.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The typical firm in the US economy
A) has some degree of market power.
B) sells its product for a price that is equal to the marginal cost of producing the last unit.
C) is perfectly competitive.
D) is a monopoly.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) In the long run, both perfectly competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms operate with excess capacity.
B) A firm operates with excess capacity when, in the long run, its level of output is below the efficient scale.
C) For any firm, efficient scale is the level of output at which the average-total-cost curve is tangent to the demand curve.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It has been said that many of the patrons in McDonald's restaurants in foreign locations are American tourists. A likely reason why many Americans dine at McDonald's while vacationing abroad is
A) they can't get enough McDonald's food when they are at home.
B) they know and trust the quality associated with the McDonald's brand name.
C) the food at local restaurants is of inferior quality.
D) that Americans, by their nature, are not very adventurous.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm, marginal revenue equals marginal cost in
A) the short run but not in the long run.
B) the long run but not in the short run.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 16-7 Consider the problem facing two firms, YumYum and Bertollini, in the frozen food market. Each firm has just come up with an idea for a new "frozen meal for two" which it would sell for $9. Assume that the marginal cost for each new product is a constant $2, and the only fixed cost is for advertising. Each company knows that if it spends $12 million on advertising it will get 1.5 million consumers to try its new product. YumYum has done market research which suggests that its product does not have any "staying" power in the market. Even though it could get 1.5 million consumers to buy the product once, it is unlikely that they will continue to buy the product in the future. Bertollini's market research suggests that its product is very good, and consumers who try the product will continue to be consumers over the ensuing year. On the basis of its market research, Bertollini estimates that its initial 1.5 million customers will buy one unit of the product each month in the coming year, for a total of 18 million units. -Refer to Scenario 16-7. If YumYum decides to advertise its product it can expect to
A) incur a loss of $15 million.
B) incur a loss of $1.5 million.
C) earn a profit of $1.5 million.
D) earn a profit of $13.5 million.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 16-6
Beatrice's Birthday Cakes is one bakery among many in the market for birthday cakes. The following table presents cost and revenue data for birthday cakes at Beatrice's. 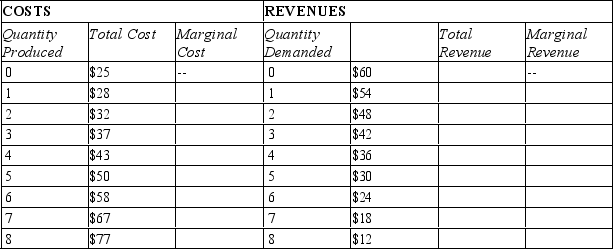 -Refer to Table 16-6. If the government required Beatrice's to produce at the efficient scale of output, how many cakes would Beatrice's sell?
-Refer to Table 16-6. If the government required Beatrice's to produce at the efficient scale of output, how many cakes would Beatrice's sell?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding monopolistic competition is not correct?
A) In the long-run equilibrium, price equals average total cost.
B) In the long-run equilibrium, firms earn zero economic profit.
C) In the long-run equilibrium, firms charge a price above marginal cost.
D) In the long-run equilibrium, firms produce a quantity in excess of their efficient scale.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to monopolistic competition,
A) both the business-stealing externality and the product-variety externality are positive externalities.
B) the business-stealing externality is a positive externality, while the product-variety externality is a negative externality.
C) the business-stealing externality is a negative externality, while the product-variety externality is a positive externality.
D) both the business-stealing externality and the product-variety externality are negative externalities.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Considering perfect competition, monopolistic competition, and monopoly, which of the market structures results in production of the welfare-maximizing level of output?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A similarity between monopoly and monopolistic competition is that in both market structures
A) strategic interactions among sellers are important.
B) there are a small number of sellers.
C) sellers are price makers rather than price takers.
D) there are only a few buyers but many sellers.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monopolistic competition is characterized by many buyers and sellers, product differentiation, and barriers to entry.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 16-6
Beatrice's Birthday Cakes is one bakery among many in the market for birthday cakes. The following table presents cost and revenue data for birthday cakes at Beatrice's.  -Refer to Table 16-6. Given the cost and revenue data, Beatrice's is
-Refer to Table 16-6. Given the cost and revenue data, Beatrice's is
A) not in a long-run equilibrium. More businesses will enter the bakery market in the long-run.
B) not in a short-run equilibrium.
C) not in a long-run equilibrium. Some businesses currently in the bakery market will exit the market in the long- run.
D) in a long-run equilibrium.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An oligopoly
A) has a concentration ratio of less than 50 percent.
B) is a price taker.
C) is a type of imperfectly competitive market.
D) has many firms rather than just one firm or a few firms.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The deadweight loss that is associated with a monopolistically competitive market is a result of
A) price falling short of marginal cost in order to increase market share.
B) price exceeding marginal cost.
C) the firm operating in a regulated industry.
D) excessive advertising costs.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Both monopolistic competition and oligopoly are market structures
A) that fail to achieve the total surplus achieved by perfect competition.
B) that feature only a few firms in each market.
C) to which the concept of Nash equilibrium is frequently applied by economists.
D) in which firms earn zero economic profit in the long run.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a monopolistically competitive market, the demand curves faced by incumbent firms are unaffected by the entry of new firms into the market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-12 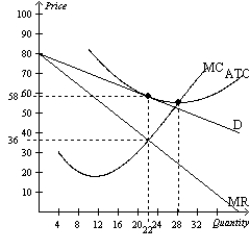 -Refer to Figure 16-12. How much cost per unit could this firm save by producing the efficient level of output rather than the profit-maximizing level of output?
-Refer to Figure 16-12. How much cost per unit could this firm save by producing the efficient level of output rather than the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $0
B) $1
C) $2
D) $3
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 580
Related Exams