A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) either A or D
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A government decision to impose a tax on the sale of plastic disposable water bottles is an example of:
A) a positive externality.
B) internalizing the externality.
C) the third-party problem.
D) an external cost.
E) the Coase theorem.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positive externalities have _________ for third parties.
A) internal costs
B) internal benefits
C) external costs
D) external benefits
E) social costs
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good that is rival and excludable is defined as a:
A) private good.
B) public good.
C) common-resource good.
D) club good.
E) government good.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the questions. 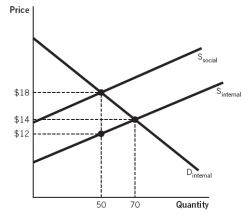 -The figure best illustrates what type of market?
-The figure best illustrates what type of market?
A) The good produced creates a positive externality.
B) The good produced creates a negative externality.
C) The good produced is a club good.
D) The good produced is a public good.
E) Firms in this industry have been given a subsidy to encourage more production.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a cost of internalizing a negative externality?
A) Less output is produced.
B) The deadweight loss is larger.
C) The level of pollution rises.
D) Taxes must increase to cover the external cost.
E) The government must pay firms to encourage them to change production techniques.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Visiting the public beach during summer is an example of an activity that is:
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) nonexcludable and rival.
D) nonrival.
E) excludable and nonrival.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your neighbor is an avid gardener who changes his flower displays four times per year and who was given the "best yard on the block" award last year. While you personally enjoy these changing flower displays, some of your neighbors have said they do not like some of the flowers your neighbor chooses to plant. For you, this is an example of:
A) a positive externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) internalizing the external cost.
E) a negative externality.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the accompanying table, where Q represents the quantity produced, internal cost and social cost are given for various quantities, and P represents the price consumers are willing to pay for various quantities. The external cost is equal to _________ per unit.
A) $60
B) $70
C) $20
D) $50
E) $30
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following scenario when answering the questions: Jones owns a factory that is dumping toxic waste into a river where Smith owns a resort. At present, Jones is -If property rights over the river are assigned to Jones, then:
A) Jones will force Smith to close his resort.
B) Smith will pay Jones up to $75 per day to install the filter.
C) Smith will pay Jones up to $125 to install the filter.
D) Jones will install a filter and pay Smith at least $75 per day.
E) Jones will not install a filter.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the accompanying figure. When a negative externality exists and the government does not intervene, which point best identifies the market equilibrium? 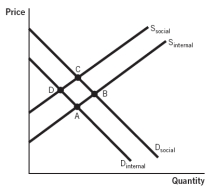
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) either C or D
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A free-rider problem exists when:
A) people receive a benefit they do not need to pay for.
B) firms impose a cost on third parties.
C) negative externalities exist.
D) a private good is produced.
E) any market is in equilibrium.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) social costs = internal costs − external costs
B) social costs = internal costs + external costs
C) internal costs = social costs + external costs
D) external costs = social costs + internal costs
E) internal costs − social costs = external costs
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a negative externality is not internalized, then the equilibrium price of the good produced is too _________ and the equilibrium quantity produced is too _________.
A) high; high
B) low; low
C) low; high
D) high; low
E) expensive; inefficient
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major reason why the market equilibrium for a manufactured good may not be efficient is:
A) there is too much government regulation.
B) property rights are not well defined.
C) there is likely to be a positive externality associated with production.
D) the industry is likely to be a monopoly.
E) the industry is producing too little output.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the accompanying figure. The market for dry-cleaning services is currently in equilibrium at point A, and the government decides to tax the stores that offer dry-cleaning services in order to improve the air quality. The new equilibrium will be at point: 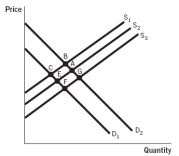
A) B.
B) C.
C) E.
D) F.
E) G.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount you pay for gasoline for your car is an example of a(n) :
A) internal cost.
B) social cost.
C) external cost.
D) third-party cost.
E) public-good cost.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
External benefits arise from the actions of:
A) firms.
B) consumers.
C) firms and consumers.
D) the government.
E) firms, consumers, and the government.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The third-party problem:
A) occurs when a market activity leads to a negative externality.
B) occurs when a market activity leads to a positive externality.
C) occurs when a market activity leads to a negative or a positive externality.
D) is the same as the free-rider problem.
E) is associated with the production of private goods but not public goods.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following scenario to answer the questions. Five fishermen live in a village and have no other employment or income-earning possibilities besides fishing. They each own a boat that is suitable for fishing but does -If four boats operate, then each boat will make a profit of:
A) $775.00.
B) $500.00.
C) $275.00.
D) $675.00.
E) $68.75.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 145
Related Exams