A) efficiency wages
B) job search
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unions
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tatiana is waiting to be recalled to a job from which she was laid off. Ivan was fired but has not looked for work during the last two months. Who does the Bureau of Labor Statistics count as "unemployed"?
A) Tatiana but not Ivan
B) Ivan but not Tatiana
C) both Ivan and Tatiana
D) neither Ivan nor Tatiana
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The natural rate of unemployment refers to the current unemployment rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Within the U.S. population, women of prime working age ages 25-54) have similar rates of labor-force participation than men of prime working age ages 25-54), regardless of race.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
People who report being not in the labor force but who, in fact, want to work but have given up trying to find a job after an unsuccessful search cause the reported unemployment rate to be lower than it would otherwise be.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From time to time, the demand for workers has risen in one region of the United States and fallen in another. This illustrates
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The destruction of manufacturing jobs and workers leaving their jobs to find better ones both contribute to frictional unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cyclical unemployment refers to the year-to-year fluctuations in unemployment around its natural rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most spells of unemployment are short, and most unemployment observed at any given time is long-term.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics' U2 measure of joblessness includes job losers and job leavers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Most people who become unemployed will soon find jobs.
B) In an ideal labor market, wages would adjust to ensure that all workers are always fully employed.
C) The unemployment rate occasionally falls to zero.
D) There are always some workers without jobs, even when the overall economy is doing well.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Minimum-wage laws affect all workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the U.S., it is illegal for employers to interfere when workers try to organize unions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More than 30 percent of U.S. workers leave their jobs in a typical month.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-3 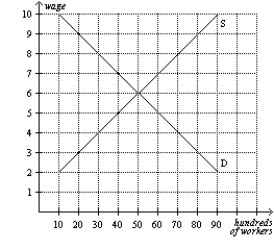 -Refer to Figure 28-3. At the equilibrium wage, how many workers are employed?
-Refer to Figure 28-3. At the equilibrium wage, how many workers are employed?
A) 0
B) 1,000
C) 5,000
D) 9,000
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to 2012 data on the U.S. population, which of the following groups of adults of prime working age ages 25-54) had the lowest unemployment rate?
A) white males
B) white females
C) black males
D) black females
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some people who are employed or who are not making serious effort to find employment will report themselves as unemployed. Some people who want to find work will be counted as out of the labor force.
A) Both the first and the second fact tend to make the reported unemployment rate lower than otherwise.
B) Both the first and the second fact tend to make the reported unemployment rate higher than otherwise.
C) The first fact tends to make the reported unemployment rate higher than otherwise, while the second fact tends to make the reported unemployment rate lower than otherwise.
D) The first fact tends to make the reported unemployment rate lower than otherwise, while the second fact tends to make the reported unemployment rate higher than otherwise.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to 2012 data on the U.S. population, which of the following was correct?
A) Adults of prime working age ages 25-54) had both higher labor-force participation rates and higher rates of unemployment compared to teenagers.
B) Adults of prime working age ages 25-54) had higher labor-force participation rates and lower rates of unemployment compared to teenagers.
C) Adults of prime working age ages 25-54) had both lower labor-force participation rates and lower rates of unemployment compared to teenagers.
D) Adults of prime working age ages 25-54) had lower labor-force participation rates and higher rates of unemployment compared to teenagers.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs, then there would be no frictional unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-4
2010 Labor Data for Adults ages 16 and older) in Meditor
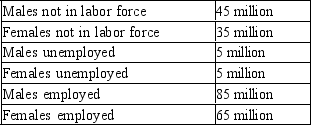 -Refer to Table 28-4. What is the adult population in Meditor?
-Refer to Table 28-4. What is the adult population in Meditor?
A) 90 million
B) 160 million
C) 230 million
D) 240 million
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 361 - 380 of 699
Related Exams