A) This reduces risk's standard deviation and firm-specific risk.
B) This reduces risk's standard deviation and market risk.
C) This raises market risk,but lowers firm-specific risk.What happens to overall risk is unclear.
D) This raises firm-specific risk,but lowers market risk.What happens to overall risk is unclear.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 27-4.The figure shows a utility function for Alex. 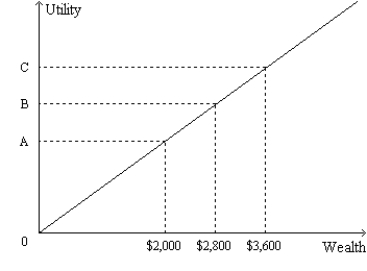 -Refer to Figure 27-4.From the appearance of Alex's utility function,we know that
-Refer to Figure 27-4.From the appearance of Alex's utility function,we know that
A) if Alex owns a house,then he definitely would buy fire insurance provided the cost of the insurance was reasonable.
B) Alex would voluntarily exchange a portfolio of stocks with a high average return and a high level of risk for a portfolio with a low average return and a low level of risk.
C) Alex is risk averse.
D) Alex is not risk averse.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 27-5.The figure shows a utility function for Dexter. 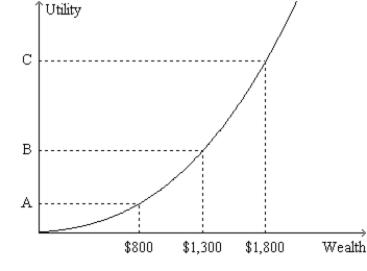 -Refer to Figure 27-5.From the appearance of the utility function,we know that
-Refer to Figure 27-5.From the appearance of the utility function,we know that
A) Dexter is risk averse.
B) Dexter gains more satisfaction when his wealth increases by X dollars than he loses in satisfaction when his wealth decreases by X dollars.
C) the property of decreasing marginal utility applies to Dexter.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 27-3
The following figure shows the utility function for Paul. 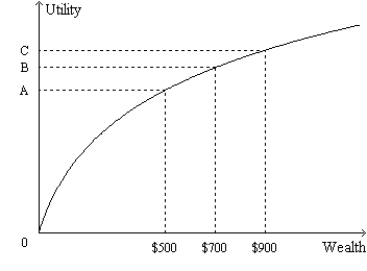 -Refer to Figure 27-3.Suppose Paul begins with $900 in wealth.Starting from there,
-Refer to Figure 27-3.Suppose Paul begins with $900 in wealth.Starting from there,
A) Paul would be willing to accept a coin-flip bet that would result in him winning $200 if the result was "heads" or losing $200 if the result was "tails."
B) the pain of losing $200 of his wealth would equal the pleasure of adding $200 to his wealth.
C) the pain of losing $200 of his wealth would exceed the pleasure of adding $200 to his wealth.
D) the pleasure of adding $200 to his wealth would exceed the pain of losing $200 of his wealth.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lori,who currently owns stock in four companies,has decided to expand her portfolio by purchasing stock in virtually every company that sells stock.In doing so,Lori will
A) increase the risk of her portfolio.
B) decrease some,but not all,of the risk of her portfolio.
C) decrease all of the risk of her portfolio.
D) leave the risk of her portfolio unchanged from its present level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tami knows that people in her family die young,and so she buys life insurance.Preston knows he is a reckless driver and so he applies for automobile insurance.
A) These are both examples of adverse selection.
B) These are both examples of moral hazard.
C) The first example illustrates adverse selection,and the second illustrates moral hazard.
D) The first example illustrates moral hazard,and the second illustrates adverse selection.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following two situations.Irene accepts a job where she will be driving in dangerous traffic,so she seeks auto insurance.After Victor buys health insurance,he visits the gym less frequently.Which of these person's actions illustrates moral hazard?
A) both Irene's and Victor's
B) Irene's but not Victor's
C) Victor's but not Irene's
D) neither Victor's nor Irene's
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 27-4.The figure shows a utility function for Alex.  -Refer to Figure 27-4.If most people's utility functions look like Alex's utility function,then it is easy to explain why
-Refer to Figure 27-4.If most people's utility functions look like Alex's utility function,then it is easy to explain why
A) people buy various types of insurance.
B) we observe a trade-off between risk and return.
C) most people prefer to hold diversified portfolios of assets to undiversified portfolios of assets.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In effect,an annuity provides insurance
A) against the risk of dying and leaving one's family without a regular income.
B) against the risk of living too long.
C) to people who are not risk-averse.
D) to people whose utility functions do not display the usual properties.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following defines an annuity?
A) For a fee,an insurance company provides you with regular income until you die.
B) A surcharge is added to life-insurance premiums paid by persons in dangerous occupations.
C) Annuity is another name for stock funds managed by mutual fund managers.
D) Annuity is another name for any diversified portfolio.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is adverse selection?
A) the risk associated with selecting stocks in only a few specific companies
B) the risk that a person will become overconfident in his ability to select stocks
C) a high-risk person being more likely to apply for insurance
D) after obtaining insurance a person having less incentive to be careful
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kayla faces risks and she pays a fee to ABC Company;in return,ABC Company agrees to accept some or all of Kayla's risks.ABC Company is
A) a mutual fund.
B) an insurance company.
C) a diversified company.
D) an equity-financed company.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Alan is risk-averse,then he will always
A) choose not to play a game where he has a 50 percent chance of winning $5 and a 50 percent chance of losing $5.
B) choose not to play a game where he has a 75 percent chance of winning $5 and a 25 percent chance of losing $5.
C) choose to play a game where he has a 55 percent chance of winning $5 and a 45 percent chance of losing $5.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) The higher average return on stocks than on bonds comes at the price of higher risk.
B) Risk-averse persons will take the risks involved in holding stocks if the average return is high enough to compensate for the risk.
C) Insurance markets reduce risk,but not by diversification.
D) Risk can be reduced by placing a large number of small bets,rather than a small number of large bets.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kyle puts a greater proportion of his portfolio into government bonds.Kyle's action
A) increases both risk and the average rate of return.
B) decreases both risk and the average rate of return.
C) increases risk,but decreases the average rate of return.
D) decreases risk,but increases the average rate of return.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chloe talked to several stockbrokers and made the following conclusions.Which,if any,of Chloe's conclusions are correct?
A) It is relatively easy to reduce firm-specific risk by increasing the number of companies one holds stock in.
B) Stock prices,even if not exactly a random walk,are very close to it.
C) Some people have made a lot of money in the stock market by using insider information,but these cases are not contrary to the efficient markets hypothesis.
D) All of Chloe's conclusions are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The largest reduction in a portfolio's risk is achieved when the number of stocks in the portfolio is increased from
A) 80 to 100.
B) 40 to 80.
C) 10 to 20.
D) 1 to 10.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a source of market risk?
A) Holding stocks in many companies carries the risk of a reduced average return.
B) Real GDP varies over time and sales and profits move with real GDP.
C) When a paper producer has declining sales,it is likely that so will other paper producers.
D) If stockholders become aggravated with the way a CEO runs a company,the price of that company's stock might fall in the stock market.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the number of corporations in a portfolio from 1 to 10 reduces
A) market risk by more than an increase from 110 to 120.
B) market risk by less than an increase from 110 to 120.
C) firm-specific risk by more than an increase from 110 to 120.
D) firm-specific risk by less than an increase from 110 to 120.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 27-1.The figure shows a utility function. 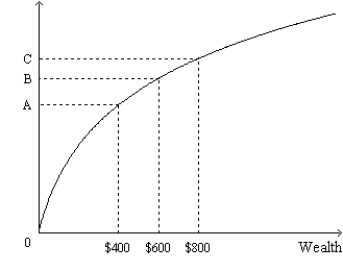 -Refer to Figure 27-1.For the person to whom this utility function applies,
-Refer to Figure 27-1.For the person to whom this utility function applies,
A) the more wealth she has,the less utility she gets from an additional dollar of wealth.
B) the more wealth she has,the more utility she gets from an additional dollar of wealth.
C) her level of satisfaction will be enhanced more by an increase in wealth from $600 to $800 than it would be by an increase in wealth from $400 to $600.
D) her level of satisfaction will be enhanced equally by an increase in wealth from $600 to $800 or by an increase in wealth from $400 to $600.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 120
Related Exams