A) only in the short run.
B) only in the long run.
C) in both the short and long run.
D) in neither the short nor the long run.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the stock market crashes,then
A) aggregate demand increases,which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply.
B) aggregate demand increases,which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply.
C) aggregate demand decreases,which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply.
D) aggregate demand decreases,which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What actions could be taken to stabilize output in response to a large decrease in U.S.net exports?
A) increase government expenditures or increase the money supply
B) increase government expenditures or decrease the money supply
C) decrease government expenditures or increase the money supply
D) decrease government expenditures or decrease the money supply
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal,in the short run a higher price level leads households to
A) increase consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
B) increase consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
C) decrease consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
D) decrease consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A surplus or shortage in the money market is eliminated by adjustments in the price level according to
A) both liquidity preference theory and classical theory.
B) neither liquidity preference theory nor classical theory.
C) liquidity preference theory,but not classical theory.
D) classical theory,but not liquidity preference theory.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events would shift money demand to the right?
A) an increase in the price level
B) a decrease in the price level
C) an increase in the interest rate
D) a decrease in the interest rate
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same,which of the following responses would we expect from an increase in U.S.interest rates?
A) Your aunt puts more money in her savings account.
B) Foreign citizens decide to buy fewer U.S.bonds.
C) You decide to purchase a new oven for your cookie factory.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the money-supply curve is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 34-3. 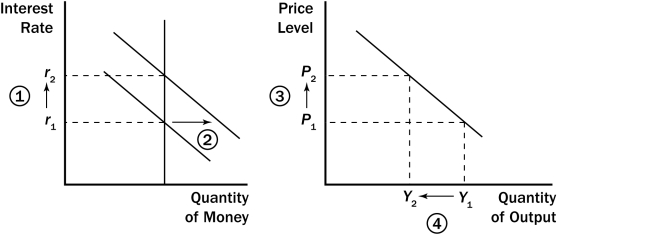 -Refer to Figure 34-3.For an economy such as the United States,what component of the demand for goods and services is most responsible for the decrease in output from Y1 to Y2?
-Refer to Figure 34-3.For an economy such as the United States,what component of the demand for goods and services is most responsible for the decrease in output from Y1 to Y2?
A) consumption
B) investment
C) net exports
D) government spending
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some economists,called supply-siders,argue that changes in the money supply exert a strong influence on aggregate supply.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In principle,the government could increase the money supply or increase government expenditures to try to offset the effects of a wave of pessimism about the future of the economy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The change in aggregate demand that results from fiscal expansion changing the interest rate is called the
A) multiplier effect.
B) crowding-out effect.
C) accelerator effect.
D) Ricardian equivalence effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,if the quantity of money supplied is greater than the quantity demanded,then the interest rate will
A) increase and the quantity of money demanded will decrease.
B) increase and the quantity of money demanded will increase.
C) decrease and the quantity of money demanded will decrease.
D) decrease and the quantity of money demanded will increase.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liquidity preference theory is most relevant to the
A) short run and supposes that the price level adjusts to bring money supply and money demand into balance.
B) short run and supposes that the interest rate adjusts to bring money supply and money demand into balance.
C) long run and supposes that the price level adjusts to bring money supply and money demand into balance.
D) long run and supposes that the interest rate adjusts to bring money supply and money demand into balance.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC = 3/5,then the government purchases multiplier is
A) 5/3.
B) 5/2.
C) 5
D) 15
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the inflation rate is zero,then the nominal and real interest rate are the same.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Employment Act of 1946
A) implies that the government should avoid being a cause of economic fluctuations.
B) implies that the government should respond to changes in the private economy to stabilize aggregate demand.
C) reflected the ideas promoted in Keynes's influential book,The General Theory of Employment,Interest,and Money.
D) All of the above are correct
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 34-1.Take the following information as given for a small,imaginary economy: • When income is $10,000,consumption spending is $6,500. • When income is $11,000,consumption spending is $7,300. -Refer to Scenario 34-1.The marginal propensity to consume for this economy is
A) 0.650.
B) 0.664.
C) 0.650 or 0.664,depending on whether income is $10,000 or $11,000.
D) 0.800.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the multiplier has a value that exceeds 1,and there are no crowding out or investment accelerator effects.Which of the following would shift aggregate demand to the right by more than the increase in expenditures?
A) an increase in government expenditures
B) an increase in net exports
C) an increase in investment spending
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest-rate effect
A) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates increase the quantity of money demanded.
B) depends on the idea that increases in interest rates increase the quantity of money supplied.
C) is the most important reason,in the case of the United States,for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
D) is the least important reason,in the case of the United States,for the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 334
Related Exams