B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-12
The following table shows the number of voters preferring various amounts of spending on a new school.
 -Refer to Table 22-12.Suppose on election day that the voters with a preference for $0.0,$2.0,$2.5,and $3.0 do not show up to vote.In this case,what is the preferred spending amount of the median voter (among those who actually cast a vote) ?
-Refer to Table 22-12.Suppose on election day that the voters with a preference for $0.0,$2.0,$2.5,and $3.0 do not show up to vote.In this case,what is the preferred spending amount of the median voter (among those who actually cast a vote) ?
A) $0.50
B) $0.75
C) $1.00
D) $1.50
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet voting paradox applies to situations in which voters
A) decide between exactly two possible outcomes.
B) decide among more than two possible outcomes.
C) as a group have transitive preferences.
D) choose the inferior candidate even though the majority preferred the better candidate.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A survey of 1,500 frequent restaurant patrons revealed that,Chang Cheng,a local Chinese restaurant,offers high-quality food at low prices.Based on one dining experience,a restaurant critic gave Chang Cheng a poor review,saying the food was not very good.As a result,you decide not to dine at Chang Cheng.This decision is an example of which of the following systematic mistakes that people make when making decisions?
A) People are overconfident.
B) People give too much weight to a small number of vivid observations.
C) People are reluctant to change their minds.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet voting paradox demonstrates that democratic outcomes do not always obey the property of
A) narrowness of preferences.
B) concavity of preferences.
C) asymmetry of preferences.
D) transitivity of preferences.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a corporation decides to include its own corporate stock as part of the compensation for its employees,it is trying to solve the
A) adverse selection problem.
B) principal-agent problem.
C) lemons problem.
D) signaling problem.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A "satisficer" is a person whose decisionmaking is the same as that predicted by mainstream economic models.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-9
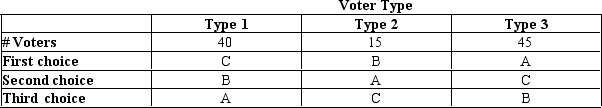 -Refer to Table 22-9.The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A,B,and C.If a Borda count election were held among these voters,giving three points to each voter's first choice,two points to the second choice,and one point to the last choice,which outcome would win the election?
-Refer to Table 22-9.The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A,B,and C.If a Borda count election were held among these voters,giving three points to each voter's first choice,two points to the second choice,and one point to the last choice,which outcome would win the election?
A) Outcome A
B) Outcome B
C) Outcome C
D) Either outcome A or outcome C since these have the same total score.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a principal-agent relationship?
A) a soccer player and her coach
B) a man and his neighbor
C) an construction worker and his foreman
D) a driver and her insurance agent
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the employer-worker relationship,the employer is regarded as the "principal" and the worker is regarded as the "agent."
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-16
Citizens in a small town are deciding how best to develop a plot of land at the center of town. They have narrowed the options to: a park, town hall, gas station, restaurant. The voters' preferences are shown in the table below.
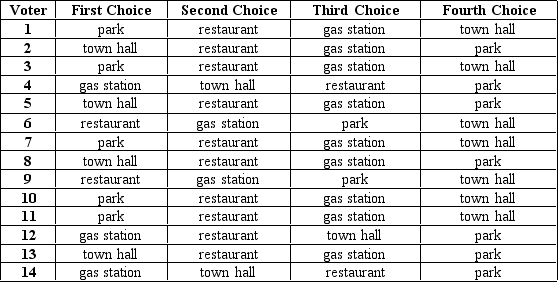 -Refer to Table 22-16.If the election is conducted by instant runoff,the final two options will be
-Refer to Table 22-16.If the election is conducted by instant runoff,the final two options will be
A) park and restaurant.
B) restaurant and town hall.
C) town hall and gas station.
D) gas station and park.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kenneth Arrow proved that the voting system that satisfied all of the properties of his "perfect" voting system was
A) one in which a single person (a "dictator") imposes his preferences on everyone else.
B) pairwise majority voting.
C) majority voting that is not pairwise.
D) None of the above is correct. Arrow proved that no voting system can satisfy all of the properties of his "perfect" system.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In view of the possible need for government action in markets where asymmetric information is a problem,which of the following is a valid concern?
A) The government rarely has more information than the private parties.
B) Private markets can sometimes deal with information asymmetries on their own.
C) The government is itself an imperfect institution.
D) All of the above are valid concerns.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the voters in a small country are choosing between two options,A and B.After the voting is complete it is discovered that option A recevied 100% of the votes with option B receiving no votes.After the vote,however,the country's leader decides that option B is better for the people and implements B rather than A.The voting system in this country fails which of Arrow's properties of a desirable voting system?
A) Unanimity
B) Transitivity
C) Independence of irrelevant alternatives
D) No dictators
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-13
The fortunate residents of Anytown have a budget surplus. The mayor decided that it is only fair to have the residents vote on what to do with the surplus. The mayor has narrowed the options down to three possible projects: a playground, a library, or a swimming pool. The voters fall into three categories and have preferences as illustrated in the table.
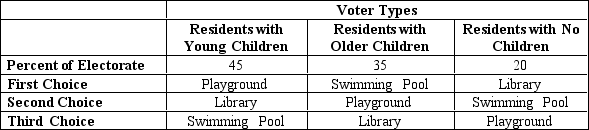 -Refer to Table 22-13.If the mayor decides to use a Borda count rather than pairwise voting,
-Refer to Table 22-13.If the mayor decides to use a Borda count rather than pairwise voting,
A) the swimming pool will win.
B) the library will win.
C) the playground will win.
D) the results will be the same as with pairwise voting.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-12
The following table shows the number of voters preferring various amounts of spending on a new school.
 -Refer to Table 22-12.What is the preferred spending amount of the median voter?
-Refer to Table 22-12.What is the preferred spending amount of the median voter?
A) $0.5
B) $1.0
C) $1.5
D) $2.0
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The criminal actions of the top managers of corporations such as Enron,Tyco,WorldCom,and Adelphia are an example of moral hazard.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-7
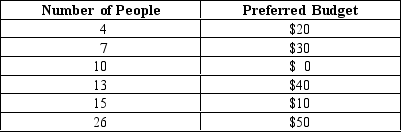 -Refer to Table 22-7.The table shows the most preferred budget of 75 voters.In an election,each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget.Which of the following statements regarding this information is true?
-Refer to Table 22-7.The table shows the most preferred budget of 75 voters.In an election,each voter will select the budget closest to his or her most preferred budget.Which of the following statements regarding this information is true?
A) In an election between a $33 budget and a $37 budget, the $33 budget will win.
B) Since the median voter theorem implies that the budget of the median voter will win the election, we would expect the overall best budget to be $25, the median of the available budgets.
C) In an election between a $10 budget and a $40 budget, the $40 budget will win.
D) Both b and c
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In American politics,we often observe that during a campaign,the Democratic and Republican positions on many issues are similar,which illustrates
A) Arrow's impossibility theorem.
B) the Condorcet paradox.
C) a Borda count.
D) the median voter theorem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of informational asymmetry?
A) A seller of a house knows more about its true condition than does a potential buyer.
B) A salesperson knows more about her efforts than does her manager.
C) A child knows more about how much time he spent playing video games while he was alone in his bedroom than do his parents.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 353
Related Exams