Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Graphically demonstrate the conditions associated with a consumer optimum.Carefully label all curves and axes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer's preferences for right shoes and left shoes can be represented by indifference curves that are
A) bowed out from the origin
B) bowed in toward the origin
C) straight lines
D) right angles
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-12 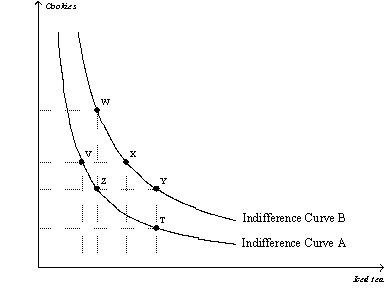 -Refer to Figure 21-12.If the consumer moves from bundle W to bundle Z,the
-Refer to Figure 21-12.If the consumer moves from bundle W to bundle Z,the
A) marginal rate of substitution remains constant.
B) total utility remains constant.
C) total utility decreases.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-7 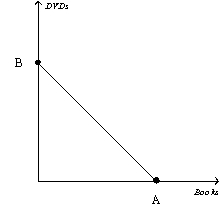 -Refer to Figure 21-7.Suppose a consumer has $200 in income,the price of a book is $5,and the price of a DVD is $10.What is the value of A?
-Refer to Figure 21-7.Suppose a consumer has $200 in income,the price of a book is $5,and the price of a DVD is $10.What is the value of A?
A) 40
B) 20
C) 10
D) 2
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a consumer spends her income on two goods: music CDs and DVDs.The consumer has $200 to allocate to these two goods,the price of a CD is $10,and the price of a DVD is $20.What is the maximum number of CDs the consumer can purchase?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 50
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of an indifference curve is
A) the rate of change of consumer's preferences.
B) the marginal rate of preference.
C) the marginal rate of substitution.
D) always equal to the slope of the budget constraint.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the two effects of a change in a price that a consumer experiences?
A) the income effect and the budget effect
B) the complement effect and the substitute effect
C) the price effect and the preference effect
D) the income effect and the substitution effect
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of consumer choice describes the
A) literal process by which people make decisions.
B) irrational decisions made by consumers on a daily basis.
C) implicit,psychological process by which people make explicit,economic decisions.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Katie wins $3 million in her state's lottery.If Katie drastically reduces the number of hours she works after she wins the money,we can infer that the income effect is larger than the substitution effect for her.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a consumer has preferences over two goods,X and Y,which are perfect substitutes.In particular,two units of X is equivalent to one unit of Y.If the price of X is $1,the price of Y is $3,and the consumer has $30 of income to allocate to these two goods,how much of each good should the consumer purchase to maximize satisfaction?
A) 30 units of X and 0 units of Y
B) 0 units of X and 10 units of Y
C) 15 units of X and 5 units of Y
D) 15 units of X and 0 units of Y
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer consumes two normal goods,sandwiches and milk.When the price of milk is $0.50 per glass,the consumer purchases 40 glasses.When the price rises to $0.65 per glass,the consumer purchases 30 glasses.We can use the information provided by the consumer's optimum choices to derive the
A) demand curve for milk.
B) demand curve for sandwiches.
C) supply curve for milk.
D) labor-leisure tradeoff.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in a consumer's income
A) increases the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
B) has no effect on the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
C) decreases the slope of the consumer's budget constraint.
D) has no effect on the consumer's budget constraint.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a consumer who purchases two goods,X and Y.If the price of good Y falls,then the substitution effect by itself will
A) cause the consumer to buy more of good Y and less of good X.
B) cause the consumer to buy more of good X and less of good Y.
C) not affect the amount of goods X and Y that the consumer buys.
D) result in an upward-sloping demand for good Y if the substitution effect is positive.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Karen,Tara,and Chelsea each buy ice cream and paperback novels to enjoy on hot summer days.Ice cream costs $5 per gallon,and paperback novels cost $8 each.Karen has a budget of $80,Tara has a budget of $60,and Chelsea has a budget of $40 to spend on ice cream and paperback novels.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Each woman faces the same budget constraint.
B) The slope of the budget constraint is the same for each woman.
C) The area underneath the budget constraint is larger for Chelsea than for Karen.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The income effect of a price change is depicted by
A) a parallel shift of the budget constraint at the old set of prices.
B) a parallel shift of the budget constraint at the new set of prices.
C) a movement along the budget constraint holding the level of satisfaction constant.
D) not observable and is therefore neither a shift nor a change in the slope of the budget constraint.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Matt has an income of $2,000,he consumes 30 units of good A and 50 units of good B.After Matt's income increases to $3,000,he consumes 25 units of good A and 95 units of good B.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Both goods A and B are normal goods.
B) Both goods A and B are inferior goods.
C) Good A is a normal good,and good B is an inferior good.
D) Good A is an inferior good,and good B is a normal good.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The consumer's optimum is where
A) MUx/MUy = Py/Px.
B) MUx/Py = MUy/Px.
C) MUx/MUy = Px/Py.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The substitution effect of a price change is depicted by a
A) movement along the budget constraint holding satisfaction constant.
B) shift in the budget constraint at the old prices.
C) movement along the consumer's new indifference curve at the new prices.
D) movement along the original indifference curve to the point where the marginal rate of substitution equals the price ratio for the new set of prices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two goods are perfect complements,the indifference curve is
A) a horizontal straight line.
B) bowed outward.
C) a downward-sloping straight line.
D) a right angle.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 321 - 340 of 492
Related Exams