A) glycolipids rather than protein.
B) transmembrane proteins with an extracellular steroid binding domain.
C) transmembrane proteins with an intracellular steroid binding domain.
D) soluble proteins in the cytoplasm.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
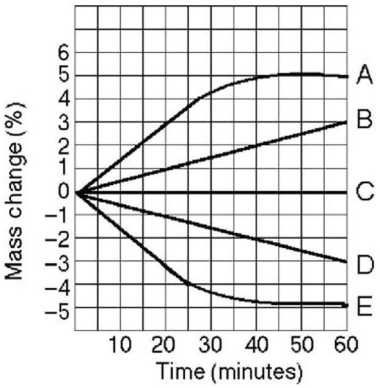 Figure 5.4
-Five dialysis bags,constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose,were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution.At 10-minute intervals,the bags were massed (weighed) ,and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed.Figure 5.4 illustrates the change in the mass of the bags over time.Which line or lines in the graph in the figure represent(s) bags that contain a solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes?
Figure 5.4
-Five dialysis bags,constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose,were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution.At 10-minute intervals,the bags were massed (weighed) ,and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed.Figure 5.4 illustrates the change in the mass of the bags over time.Which line or lines in the graph in the figure represent(s) bags that contain a solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes?
A) A and B
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) D and E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electrochemical gradient across a membrane would generally be increased by which of the following membrane proteins?
A) a calcium ion channel
B) a sucrose-proton cotransporter
C) a hydrogen ion pump
D) a sodium ion channel
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Submerging a plant cell in distilled water will result in
A) plasmolysis of the cell.
B) lysis of the cell membrane.
C) bursting of the cell.
D) the cell becoming turgid.
E) the cell becoming flaccid.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes adds a phosphate group to target proteins?
A) kinase
B) phosphatase
C) G protein-coupled receptor
D) adenylyl cyclase
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules are localized on the exterior of a phospholipid bilayer?
A) saturated fatty acids
B) unsaturated fatty acids
C) phosphate groups
D) cholesterol
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease in humans in which the CFTR protein,which functions as a chloride ion channel,is missing or nonfunctional in cell membranes.The CFTR protein belongs to what category of membrane proteins?
A) gap junctions
B) carrier proteins
C) electrogenic ion pumps
D) cotransporters
E) hydrophilic channels
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure suggests that membranes
A) are composed of a fluid bilayer of fatty acids with proteins associated on the outer and inner surfaces.
B) are composed of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
C) are composed of a single fluid layer of phospholipids and proteins.
D) are composed of a fluid phospholipid bilayer sandwiched between two layers of hydrophilic proteins.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
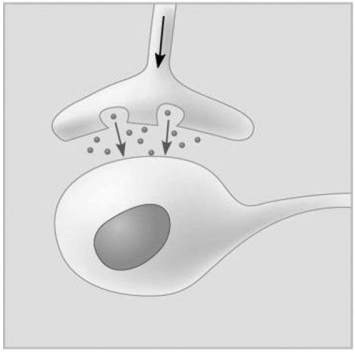 Figure 5.5
-Which of the following types of signaling is represented in Figure 5.5?
Figure 5.5
-Which of the following types of signaling is represented in Figure 5.5?
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) hormonal
D) synaptic
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Submerging a red blood cell in distilled water will result in
A) plasmolysis of the cell.
B) lysis of the cell.
C) the cell becoming turgid.
D) the cell becoming flacid.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sugars associated with glycoproteins and glycolipids of animal cell membranes
A) serve as an energy source for the cell.
B) serve as markers that distinguish one cell from another.
C) decrease membrane fluidity at high temperatures.
D) maintain membrane fluidity at low temperatures.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels,the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway?
A) receptor
B) relay molecule
C) signal molecule
D) transducer
E) molecule protein
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug designed to inhibit the response of cells to the steroid hormone aldosterone would almost certainly result in which of the following?
A) lower cytoplasmic levels of cAMP
B) an increase in receptor tyrosine kinase activity
C) a decrease in transcriptional activity of certain genes
D) a decrease in G protein activity
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At human body temperature (37°C) ,cholesterol in membranes functions to
A) make the membrane less fluid by restricting the movement of phospholipids.
B) make the membrane more fluid by stimulating the movement of phospholipids.
C) facilitate cell-cell interactions by binding to receptors on neighboring cells.
D) make the membrane more fluid by crowding integral membrane proteins into restricted areas.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
A) large hydrophobic
B) small hydrophobic
C) large polar
D) small ionic
E) large and hydrophilic
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a carrier protein in a plasma membrane?
A) It is a peripheral membrane protein.
B) It exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule.
C) It requires the expenditure of cellular energy to function.
D) It works against a concentration gradient.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When biological membranes are frozen and then fractured,they tend to break along the middle of the bilayer.The best explanation for this is that
A) the integral membrane proteins are not strong enough to hold the bilayer together.
B) water that is present in the middle of the bilayer freezes and is easily fractured.
C) the hydrophobic interactions between ends of the fatty acid tails of the two phospholipid monolayers are the weakest interactions in the membrane.
D) the carbon-carbon bonds of the phospholipid tails are easily broken.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell against the phosphate concentration gradient.The energy for phosphate import is provided by a pH gradient across the membrane (lower pH outside the cell than inside the cell) ,rather than by ATP hydrolysis.The bacterial phosphate transport system is an example of
A) passive diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) active transport.
D) cotransport.
E) receptor-mediated endocytosis.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes includes all the others?
A) osmosis
B) diffusion of a solute across a membrane
C) passive transport
D) transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Theoretically,how might researchers disrupt signal transduction pathways as possible treatments for cancer?
A) alter G protein-coupled receptors involved in cell cycle regulation to be active in the absence of their normal signaling molecules
B) inactivate epinephrine receptors on cancer cells
C) disrupt the function of protein kinases involved in cell cycle regulation
D) stimulate production of cAMP in cancer cells
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 86
Related Exams